I was approached by many educators in my teaching context asking about web2.0. What is it? Why is it called web2.0? Intuitively because there was a web 1.0 :)
To explain what web2.0 is, I should show you what web1.0 is and how they differ and how web2.0 affords an innovative learning based on collaboration and sharing of knowledge.
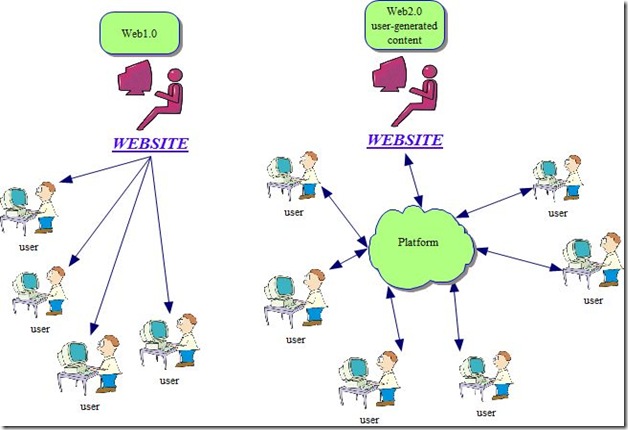
The model below roughly shows how web1.0 differs from web2.0.
Web1.0 was used in education and language learning for drills and practice. The “drill” and “practice” nouns lend themselves well to behaviorist theory of learning. It can be seen as the PP approach too where PP refers to Present then Practice. The website Presents and learners, especially language learner, Practice but with little or no third P (Produce).
Web2.0, however, has arrived due to technological advances.
An impressive range of web2.0 collection of websites can be found at http://go2web20.net .
The most important feature of web2.0 is that users can collaborate and build on each others’ knowledge. If you access the internet now, you would find unlimited amount of information that would not be possible without users pouring their contents;Therefore the term, user-generated content!! Website companies then rely on the user for their success. The more users generate content, the more the website company is successful.
I am sure that all of you now generate content in the web2.0. Social networking websites such as facebook, myspace, and ning; photo sharing websites such as flickr; social bookmarking websites such as delicious and diigo; professional netoworking websites such as linkdein; video sharing websites such as youtube and vimeo and much more rely on the user, you, to ensure their success. In fact you can hardly now see any website that is static termed as web1.0.
The following collage shows some of the most famous web2.0 applications. The collage was created using Picasa, a free photo editing application owned by Google.

How Is Web2.0 Used in Education and Language Learning?
The increasing presence of the internet in schools and at home encouraged educators to harness the power of web2.0, which is web based and needs access to the internet. The good thing is that web2.0 applications are free!! At least most of them are:)
Students can collaborate on projects, create images, edit videos, write blogs, and share bookmarks using web2.0. Yet, web2.0 is a tool and teachers should know how to harness its power based on methodology and research and not on technological aspects. Moreover, like any tool, web2.0 tools are diverse and each tool lends itself to a language skill or, in case of overall education, lends itself to particular subjects.
The following table lists a sample of some of the most famous established and emergent web2.0 tools and what linguistic skills or any other skill each tool affords, under the guidance of the teacher.
( Click each logo to link to its website).
The above table lists only a slim portion of the available web2.0 tools. I shall list a more comprehensive web2.0 tools in a later post. Teachers should be aware that students should be trained on the above tools before including them in education and the language curriculum. Web2.0 technology has been proven to increase learner autonomy, creativity , and interactivity.
I hope this post was useful to language teachers and educators who are novice at implementing technology in their teaching contexts.
Your comments are always welcome. If you want to share your own experience of any web2.0 tool in your teaching context please do share !!!
To explain what web2.0 is, I should show you what web1.0 is and how they differ and how web2.0 affords an innovative learning based on collaboration and sharing of knowledge.
The model below roughly shows how web1.0 differs from web2.0.

Web1.0 refers to :
- slow connection (modem)
- HTML websites
- One to many communication
- Static Websites
Web1.0 was used in education and language learning for drills and practice. The “drill” and “practice” nouns lend themselves well to behaviorist theory of learning. It can be seen as the PP approach too where PP refers to Present then Practice. The website Presents and learners, especially language learner, Practice but with little or no third P (Produce).
Web2.0, however, has arrived due to technological advances.
Some of web2.0 features are:
- fast internet connection (dsl, fiber optics, cables)
- Websites based on Advanced coding and languages such as XHTMl , ajax, Ruby on the Rails
- many to many users ( The website supplies the platform and users create content)
- dynamic websites including comments features, sharing files and multimedia
- rss aggregation
- little knowledge of html on part of the users to be able to supply content
An impressive range of web2.0 collection of websites can be found at http://go2web20.net .
The most important feature of web2.0 is that users can collaborate and build on each others’ knowledge. If you access the internet now, you would find unlimited amount of information that would not be possible without users pouring their contents;Therefore the term, user-generated content!! Website companies then rely on the user for their success. The more users generate content, the more the website company is successful.
I am sure that all of you now generate content in the web2.0. Social networking websites such as facebook, myspace, and ning; photo sharing websites such as flickr; social bookmarking websites such as delicious and diigo; professional netoworking websites such as linkdein; video sharing websites such as youtube and vimeo and much more rely on the user, you, to ensure their success. In fact you can hardly now see any website that is static termed as web1.0.
The following collage shows some of the most famous web2.0 applications. The collage was created using Picasa, a free photo editing application owned by Google.

How Is Web2.0 Used in Education and Language Learning?
The increasing presence of the internet in schools and at home encouraged educators to harness the power of web2.0, which is web based and needs access to the internet. The good thing is that web2.0 applications are free!! At least most of them are:)
Students can collaborate on projects, create images, edit videos, write blogs, and share bookmarks using web2.0. Yet, web2.0 is a tool and teachers should know how to harness its power based on methodology and research and not on technological aspects. Moreover, like any tool, web2.0 tools are diverse and each tool lends itself to a language skill or, in case of overall education, lends itself to particular subjects.
The following table lists a sample of some of the most famous established and emergent web2.0 tools and what linguistic skills or any other skill each tool affords, under the guidance of the teacher.
( Click each logo to link to its website).
| Web2.0 Tool | Features | Implications for Language Learning |
Wikis   | A wiki is a website where it is possible for members to modify content easily. Members can edit and modify each others’ input. Wikis usually are chaotic so it is advised that the teacher moderate it and modify what is not relevant or inappropriate. | Students can use it to collaborate on projects. For instance, they can start a book project where they initiate the idea of the book and edit for each other, add content, correct, and collaborate. Wikis lend themselves specifically for writing skills. The final product can be made public for the world to see. This gives motivation for students in learning. |
Podcasts    | A website where users create and upload podcasts. Podcasts are audio recorded by any digital recorder or using a pc and a mic. Major universities and educational institutions have podcasts ready to download. | Language teachers can use it with their students to enhance pronunciation, communication, and motivation. Students can, for instance, interview any of their classmates, teachers, staff, or any other person on a certain issue. They can even start a school radio station as some schools have lately done. The audio input on the pc can be edited using an audio editing software such as audacity, an open source free audio editing tool that rivals commercial editing software. Podcast can be shared on the internet and downloaded to PCs or mobile devices such as iphone. Teachers can also podcast whole lessons and lectures for their students to listen on-the-move http://www.podcastdirectory.com/ is a directory for most podcasts (also called internet radio) |
Blogging    | A blog is the blending of two word web and log.Posts by users appear in a reverse chronological order .Blogging needs no html knowledge and some of its features are the ability of commenting on posts, installing plugins and widgets, embedding videos… Websites can install a blog onto their servers now to make them dynamic and interact with users. The best known blogging software is the free wordpres. | Language teachers can have students start their own blogs. Each blog should discuss a certain issue ,e.g. hiking, music, tv shows, technology, and much more. Teachers can also set up a class blog and make students members so they can post and comment on each others’ posts. Students can share learning resources, aid each other, and share links to websites. Blogging helps students with writing and reading skills. It , as well, provides students with real international audience who can comment on their posts. |
Microblogging   | Microblogging is blogging with a limited number of characters. The best know microbloggin platform is twitter where any user can tweet a 140 characters. The simple question of twitter is “What are you doing now?” Tweeting can ranger from silly updates such as “ I am sleepy now” to significant tweets such as “ US Department of Edu. research finds that online learning beats f2f (link to website)”. In twitter, the user can follow the updates of whoever he or she wants. Twitter has become so famous that even Oprah, President Obahama, and Queen Rania tweet. | Students can tweet on their current status and can share what they discovered on the WWW using the link feature or even reflect on their own learning. They can be given the choice to follow their favorite singers’ updates for example then create a report on their current lives. Microblogging has been proven by research that it enhances writing, and cognition. Edmodo is a microblogging platform designed specifically for education. If you wan to know more on edmodo read my earlier post. |
Social Networking    | These are websites that provide platform for users to create their own network of friends and other users of mutual interest. Users range from professionals to primary school students. Each user can share, discuss, and comment on their connection’s activities, updates, blogs, videos, or photos. Users can share files and multimedia form all over the globe. one example of a ning professional network is classroom20 where 25000+ teachers share and collaborate on issues related on using technology in education. | Students can create their own social network in facebook and myspace. They can interact with other users using features such as commenting, updating, tagging photos and videos. Ning is a social network that lends itself to education more than the above ones. Teachers can setup private networks or public where students meet and collaborate on learning issues. Social networking not only enhances learners’ writing and reading skills but also it motivates them and increases their interculturality. |
The above table lists only a slim portion of the available web2.0 tools. I shall list a more comprehensive web2.0 tools in a later post. Teachers should be aware that students should be trained on the above tools before including them in education and the language curriculum. Web2.0 technology has been proven to increase learner autonomy, creativity , and interactivity.
I hope this post was useful to language teachers and educators who are novice at implementing technology in their teaching contexts.
Your comments are always welcome. If you want to share your own experience of any web2.0 tool in your teaching context please do share !!!
An extremely useful and succinct summary of the web 2.0 tools. Very easy to follow! Thanks Ammar
ReplyDeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteAn amazing post that makes, web 2.0 usages easy. Thanks for sharing.
Essay Writing Service